Stream Statistics
The following table lists the Streaming Output statistics:
Tip
Scroll down for SRT graphical statistics example.
SRT streams include a graphical statistics display as shown in the following example of redundant transport paths:
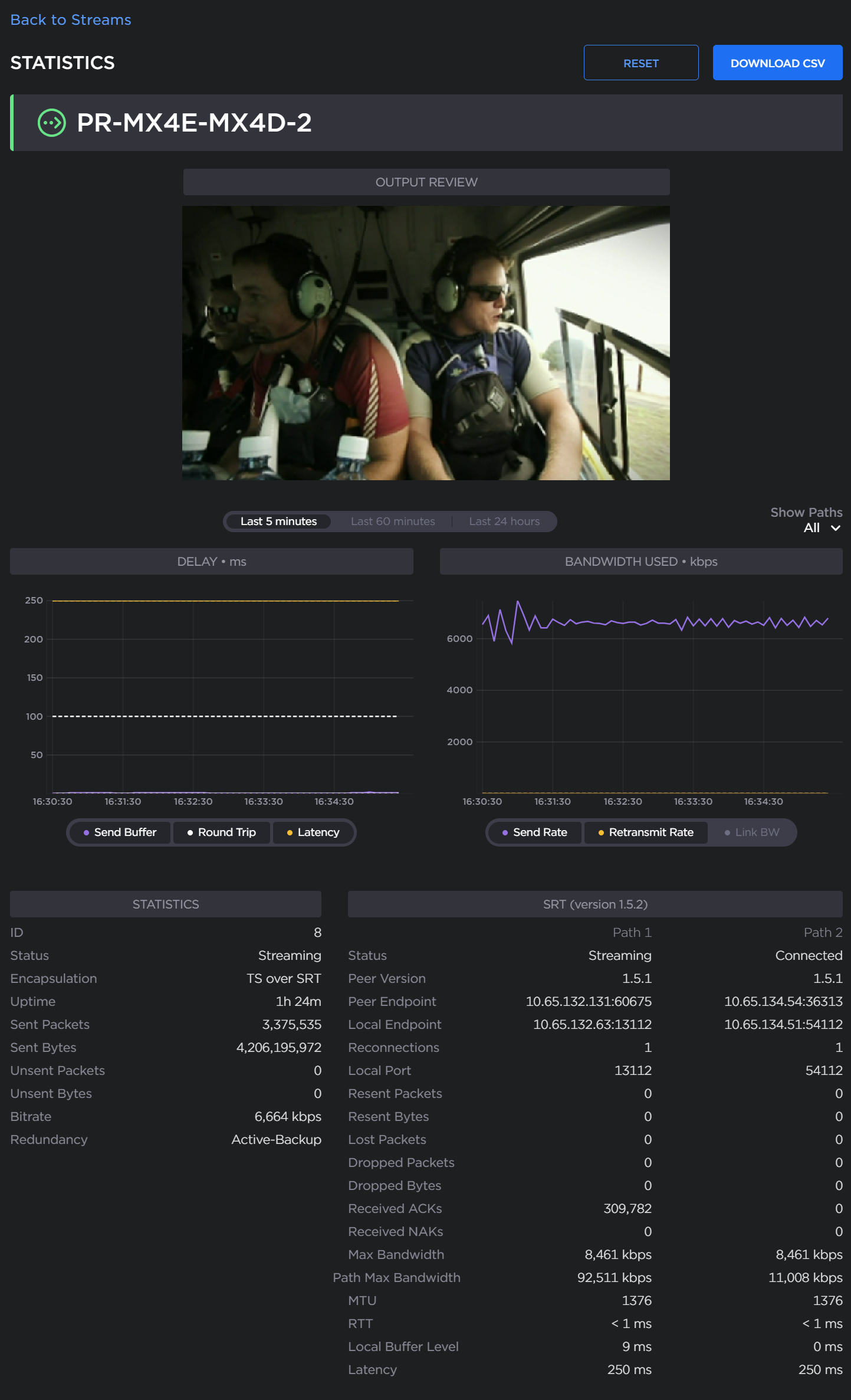
Note
The Link Bandwidth is an estimate of the actual link bandwidth.
See Configuring SRT Path Redundancy for more on the detailed SRT stream statistics.
Related Topics
