Video Encoder Settings
The following tables list the Video Encoder controls and settings:
Video Encoder Setting | Default | Description/Values |
|---|---|---|
Input | The Video Input port for the encoder (Read-only since the Makito X1 provides one BNC input). | |
BNC-1 |
| |
FIR Filter | Disabled | Check this checkbox to enable Input Image Filtering for the input interface. This parameter filters the video input and removes noise in order to optimize the compression of the image and to enhance the overall quality of the coded video stream. Tip Input Image filtering is useful with sources that are monochrome, noisy and difficult to encode because the content is detailed. Enabling this parameter filters the image in order to reduce the amount of noise, resulting in better quality video after the encoding since less noise is being compressed into the stream. |
Input Format | n/a | This is the input signal auto-detected from the video source. It includes the number of pixels per line, whether the video is interlaced or progressively scanned (indicated by i or p), and the number of frames per second. Note If the signal cannot be detected (or is outside the supported range), the Input Format will be Unknown. |
Video Encoder Setting | Default | Description/Values |
|---|---|---|
Codec Algorithm | HEVC | Select the codec algorithm for the encoder:
|
Encoding Profile | Main | Select the application profile class for the encoder: |
(AVC/H.264 only)
| ||
(HEVC/H.265 only)
| ||
Chroma Subsampling | 4:2:0 8-bit | Select the Chroma Subsampling for the encoder:
|
Dynamic Range | (10-bit Chroma Subsampling must be selected) Select to configure the encoder to detect the inbound High Dynamic Range (HDR) transfer function signaling and forward that information within the encoded stream.
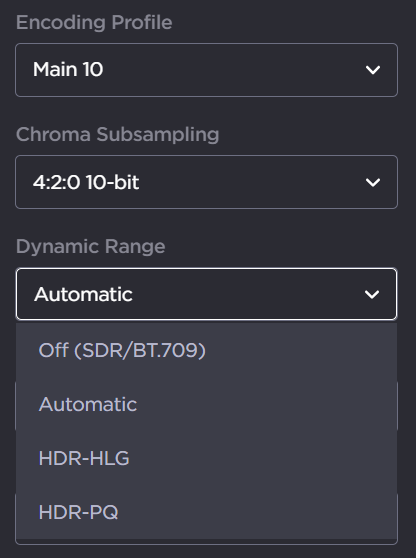 | |
Rate Control | CBR | Select the Rate Control for the encoder:
|
Max Bitrate | Auto | (Rate Control must be CVBR) Enter the maximum video bitrate for the encoder: 32 to 120,000 Kbps When set to Auto, the Max Bitrate is the same as the configured Bitrate below. |
Bitrate | 6000 kbps | Enter the video bitrate for the encoder: 32 to 120,000 kbps |
Partial Image Skip | Disabled | (Rate Control must be CBR) Select whether to allow the encoder to skip part of the image in order to respect the bitrate limit. This parameter is used to create streams that are CBR-compliant according to the MPEG-2 TS specification. One aspect of this functionality is to have the video encoder control the total number of bits generated across a GOP sequence so that all the NALs in each GOP have roughly the same amount of bits and to avoid overflowing the coded picture buffer (CPBuf). One method of doing this is the limit the size of individual video NALs associated with a frame when the bit budget is being over-subscribed. In essence the video encoder will skip encoding part of the image in order to not oversubscribe the bit budget for the GOP sequence. Partial Image Skip is useful for ISR customers who have multiple streams being decoded by various decoders with limited network bandwidth resources. In order to ensure that all the streams stay within their bandwidth budgets, they use CBR implementations of video encoders to constrain their output streams to adhere to specified bandwidth limits. Note Intra-Refresh is not an option in these situations since they use multiple types of decoders and not all of them support decoding Intra-Refresh content. |
Resolution | Automatic | Select the stream output resolution (i.e., the number of lines per frame and pixels per line to be encoded):
Note Manually selecting a coded picture resolution will increase the video encoder latency by one (1) frame period. |
Resizing | Scale | (Resolution cannot be set to Automatic and must be less than the Input Format) Select whether to scale or crop the input to the desired resolution:
By default, input is scaled to the specified output resolution. |
Frame Rate | Automatic | Select the coded picture frame rate per second:
Note The frame rate cannot exceed the input frame rate. |
Framing | IP | Select the video compression mode for the encoded video:
Note B frames require a Main Profile decoder. B frames provide more quality as the encoding is more efficient; thus more details can be rendered in the same bandwidth/bitrate. Tip When B frames are used, the GOP may be rounded up to make the sequence end with a P frame. |
Scene Change Detection | Disabled | Check this checkbox to enable scene change detection. When enabled, this feature automatically detects significant scene changes in the source video and generates an I-Frame to reduce trailing artifacts. The scene change percentage (i.e. the percentage of the scene that changes in order for the encoder to detect it) is set to 50% by default, and can be altered using the slider. 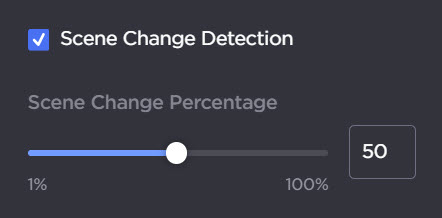 |
Intra-Refresh | Disabled | Check this checkbox to enable Intra-refresh video encoding support. Intra-refresh is a video encoding mode of operation in which no distinct IDR frame is sent in the video elementary stream. Instead, the macro-blocks that make up the IDR frame are sent gradually within a certain time so that the entire video reference frame is rebuilt (at the decoder) within the number of frames specified by the Intra Refresh Rate parameter. Intra-refresh minimizes latency, smooths the video bitrate, and minimizes GOP pulsing artifacts. Tip Intra-refresh requires that decoders that do not support random access points be started first. |
GOP Size | 120 | (Intra-Refresh must be disabled) Enter the Group of Pictures size for the encoded video. 1..1000 |
Slices | 1 | Configures the encoder to use multiple slices per frame instead of the normal 1 slice per frame encoder configuration. Encoding latency is improved since encoded slices can be transmitted on the network without having to wait for the whole frame to be encoded. 1..11 Setting the number of slices to 2 or higher will automatically enable slice-based video capture and encoding, resulting in even lower end-to-end latency. Streams with multiple slices will remain compliant with H.264 and H.265 standards, and will still be compatible with standard receivers and decoders. Note Latency improvements are only seen on decoders that do not buffer entire video frames before decoding and can actually decode and output slices. Multiple slices cannot be used in conjunction with Partial Image Skip or Framing containing B-frames (IBP, .... IBBBBP). |
Closed Captioning | Disabled | (Optional) Check this checkbox to enable Closed Captioning on the output Stream. |
TimeCode Source | None | Timecodes are used to mark video frames, mainly for editing purposes. This field either disables timecoding, or selects the source to “timecode” the encoded video frame. The following selections are available:
|
Aspect Ratio | Automatic | Specifies the aspect ratio of the video source and signals it into the MPEG stream:
Note WSS is only supported with analog PAL video; AFD is only supported with SD-SDI video. |
Related Topics
