Section 2 Source
Creating a Channel | |
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | |
2 | Source |
3 | Protocol Settings (SRT only) |
4 | |
The available configuration options depend on the selected source streaming protocol.
The following figure shows the Source section of the Route screen for a TS over UDP route. The numbered callouts in the figure indicate the step number in this procedure.
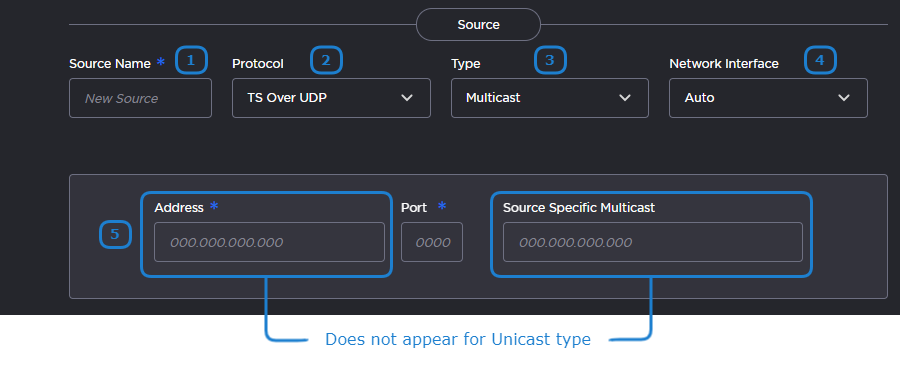
Enter the desired name for the source stream.
Tip
Keep the name under 30 characters to have the entire name displayed in the Route List screen. Longer names are still visible, but you must hover your cursor over the name for a popup to appear displaying the entire name.
In the Protocol dropdown, select TS over UDP.
Select Unicast or Multicast in the Type dropdown.
Choose the desired network interface to use for this route in the dropdown. Available options depend on the hardware configuration.
If you chose Unicast in the previous step, enter the listening port number.
If you chose Multicast in the previous step, enter the multicast IP address and listening port number. Also, optionally, enter the IGMP v3 source address in the Source Specific Multicast field.
Note
IGMPv3 Source Specific Multicast reception allows input streams to join a multicast group and filter the input streams based on a specific source IP address. Only streams originating from the specified source IP are forwarded to HMG/HSG, which allows HMG/HSG to quickly and easily select an input stream in environments with many sources sharing a common multicast IP. See IETF RFC 3376 for more details.
As there are no additional protocol settings to configure, continue to Section 4 Destinations.
The following figure shows the Source section of the Route screen for a TS over SRT route. The numbered callouts in the figure indicate the step number in this procedure.
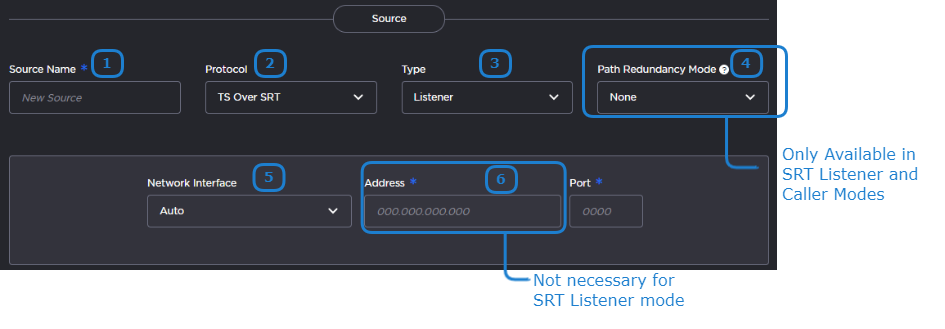
Enter the desired name for the source stream.
Tip
Keep the name under 30 characters to have the entire name displayed in the Route List screen. Longer names are still visible, but you must hover your cursor over the name for a popup to appear displaying the entire name.
In the Protocol dropdown, select TS over SRT.
Specify the SRT connection mode in the Mode dropdown:
Caller — The SRT stream acts like a client and connects to a server listening and waiting for an incoming call.
Listener — The SRT stream acts like a server and listens and waits for clients to connect to it.
Rendezvous — Allows calling and listening at the same time.
Tip
To simplify firewall traversal, Rendezvous mode allows the encoder and decoder to traverse some firewall configurations without the need for IT to open a port.
If you chose Caller or Listener mode, select whether to use SRT Path Redundancy. If so, select the desired mode and use the +/– buttons next to each network address to add/subtract network paths when completing the following two steps. See Using Path Redundancy with SRT Streaming for more details.
Any (SRT Listener only) — Automatically use the path redundancy mode defined by SRT Caller.
Active-Active — Stream packets are sent on all defined network paths. The listener uses the first received stream packets and ignores the duplicate packets received from the other network paths. This mode maintains low latency at the expense of network bandwidth.
Active-Backup — Stream packets are sent only on the main network path. If the main path fails, one of the backup paths begins transmission of the stream. This mode saves network bandwidth at the expense of latency.
None — SRT Path Redundancy disabled.
Choose the desired Network Interface to use in the dropdown. Available settings depend on the hardware configuration.
If using SRT Listener mode, enter the listening port.
If using SRT Caller or Rendezvous mode, enter the source stream address and port.
Continue to Section 3 Protocol Settings.
The following figure shows the Source section of the Route screen for a TS over RTP route. The numbered callouts in the figure indicate the step number in this procedure.
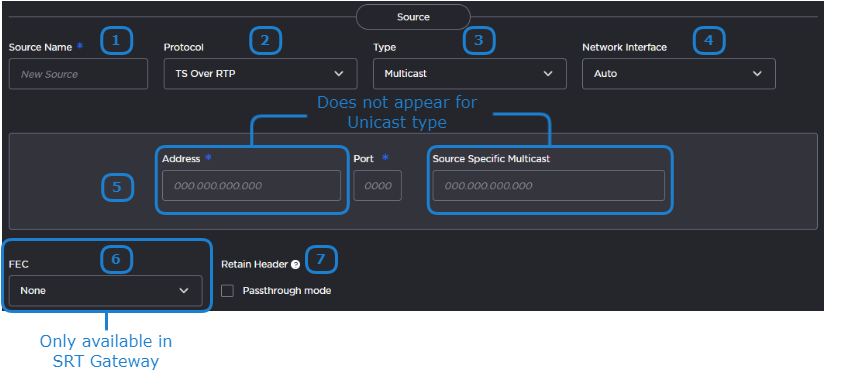
Enter the desired name for the source stream.
Tip
Keep the name under 30 characters to have the entire name displayed in the Route List screen. Longer names are still visible, but you must hover your cursor over the name for a popup to appear displaying the entire name.
In the Protocol dropdown, select TS over RTP.
Select Unicast or Multicast in the Type dropdown.
Choose the desired network interface to use for this route in the dropdown. Available options depend on the hardware configuration.
If you chose Unicast in a previous step, enter the listening port number.
If you chose Multicast in a previous step, enter the multicast IP address and listening port number. Also, optionally, enter the IGMP v3 source address in the Source Specific Multicast field.
Tip
An even-numbered port is required for RTP, as recommended in RFC 3550. (The next odd-numbered port is typically reserved for RTCP messages.)
Note
IGMPv3 Source Specific Multicast reception allows input streams to join a multicast group and filter the input streams based on a specific source IP address. Only streams originating from the specified source IP are forwarded to HMG/HSG, which allows HMG/HSG to quickly and easily select an input stream in environments with many sources sharing a common multicast IP. See IETF RFC 3376 for more details.
Select whether PRO-MPEG FEC is enabled or not.
Note
PRO-MPEG FEC is available only on Haivision SRT Gateway.
If you plan to tunnel the RTP stream through SRT, check the Retain Header > Passthrough mode checkbox. See Tunnelling an RTP Stream Through SRT for more details.
Note
PRO-MPEG FEC is not supported when Passthrough mode is enabled.
As there are no additional protocol settings to configure, continue to Section 4 Destinations.
The following figure shows the Source section of the Route screen for an RTMP route. The numbered callouts in the figure indicate the step number in this procedure.
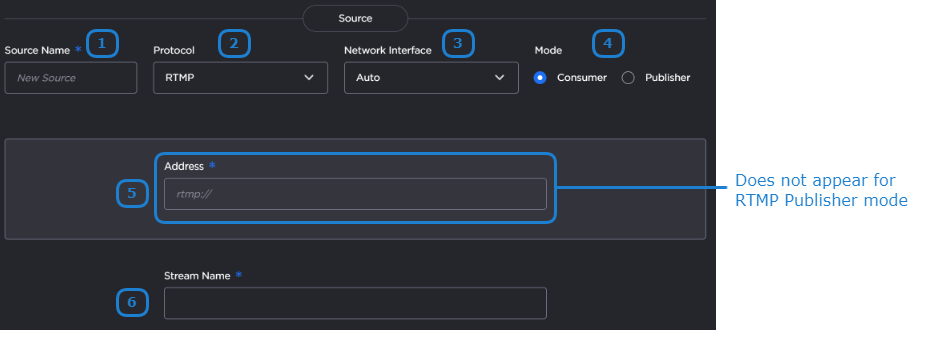
Enter the desired name for the source stream.
Tip
Keep the name under 30 characters to have the entire name displayed in the Route List screen. Longer names are still visible, but you must hover your cursor over the name for a popup to appear displaying the entire name.
In the Protocol dropdown, select RTMP.
Choose the desired network interface to use for this route in the dropdown. Available options depend on the hardware configuration
Select the mode for connection to the RTMP stream:
Consumer — Stream available for Media Gateway/SRT Gateway to access on an RTMP server.
Publisher — Stream sent directly to the Media Gateway/SRT Gateways's IP address. See Connecting an RTMP Publisher Source for further details regarding RTMP Publisher mode.
If using RTMP Consumer mode, enter the source stream address, including the port number.
Important
This is the RTMP source address, not the address of your HMG/HSG.
Enter the RTMP stream name.
Continue to Section 3 Protocol Settings.
The following figure shows the Source section of the Route screen for an RTSP route. The numbered callouts in the figure indicate the step number in this procedure.
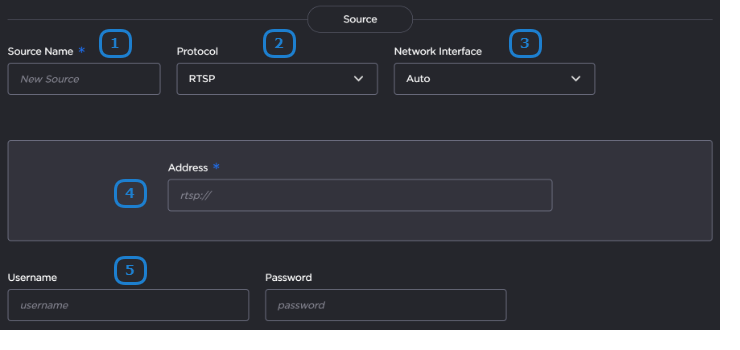
Enter the desired name for the source stream.
Tip
Keep the name under 30 characters to have the entire name displayed in the Route List screen. Longer names are still visible, but you must hover your cursor over the name for a popup to appear displaying the entire name.
In the Protocol dropdown, select RTSP.
Choose the desired network interface to use for this route in the dropdown. Available options depend on the hardware configuration.
Enter the source stream address, including the port number.
Specify the username and password for the RTSP stream.
Note
Depending on the stream, the username/password may not be required.
Continue to Section 3 Protocol Settings.
